FACILITIES AND SERVICES
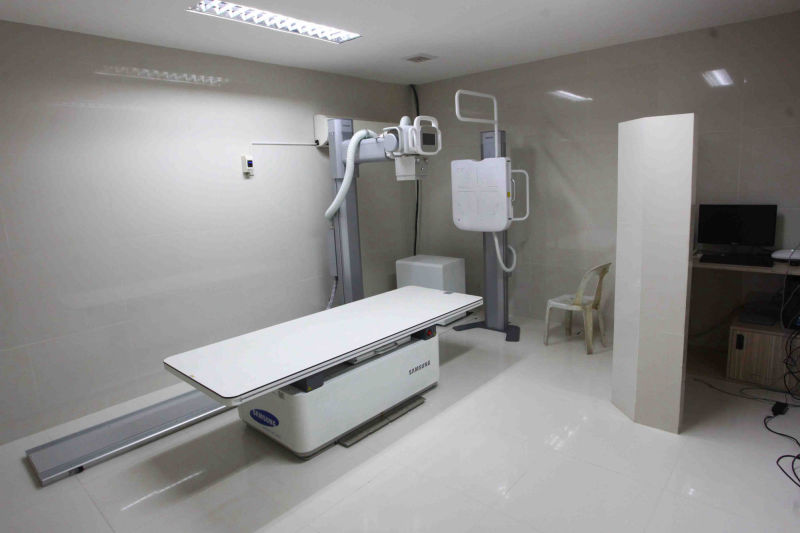
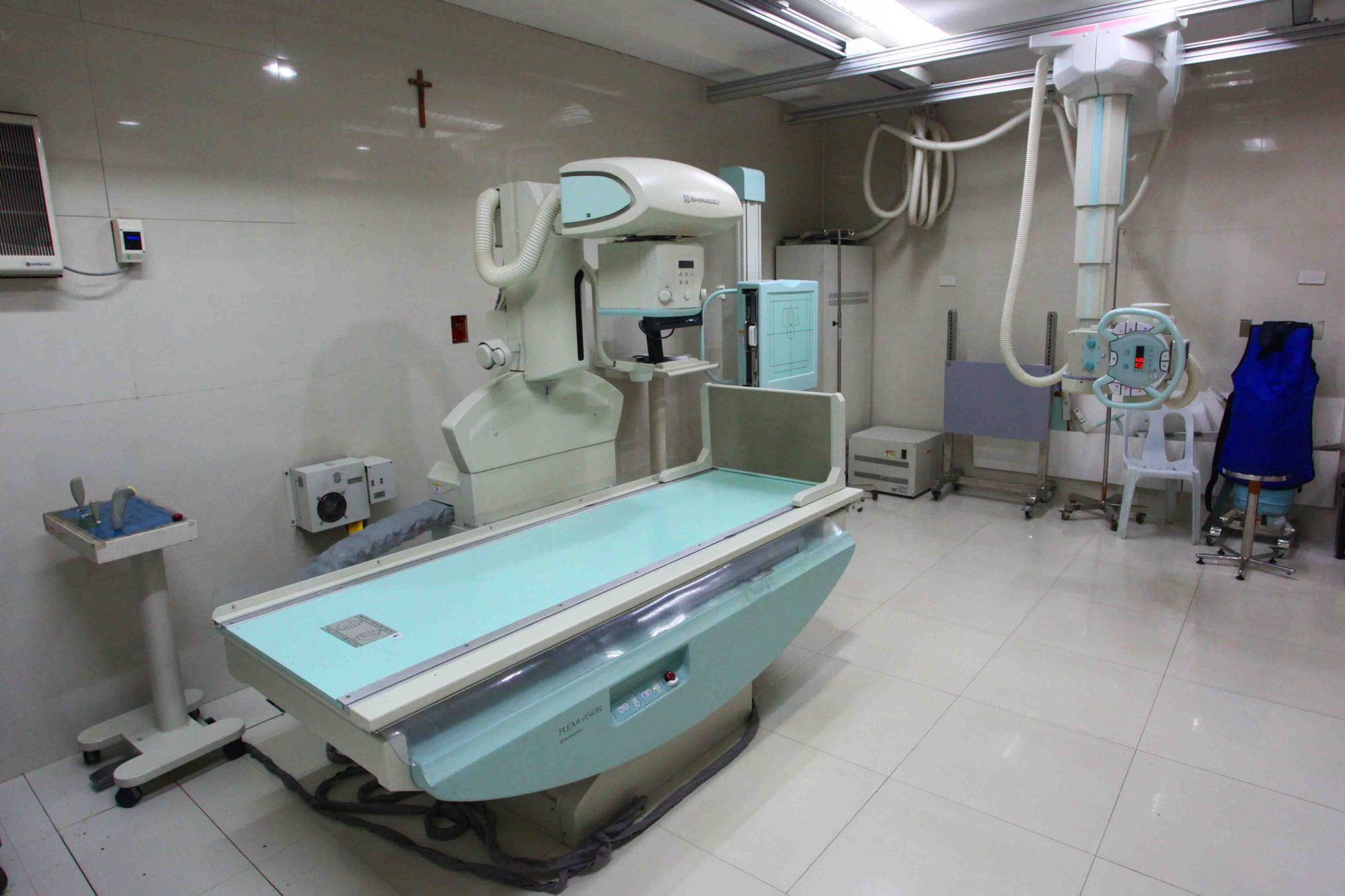
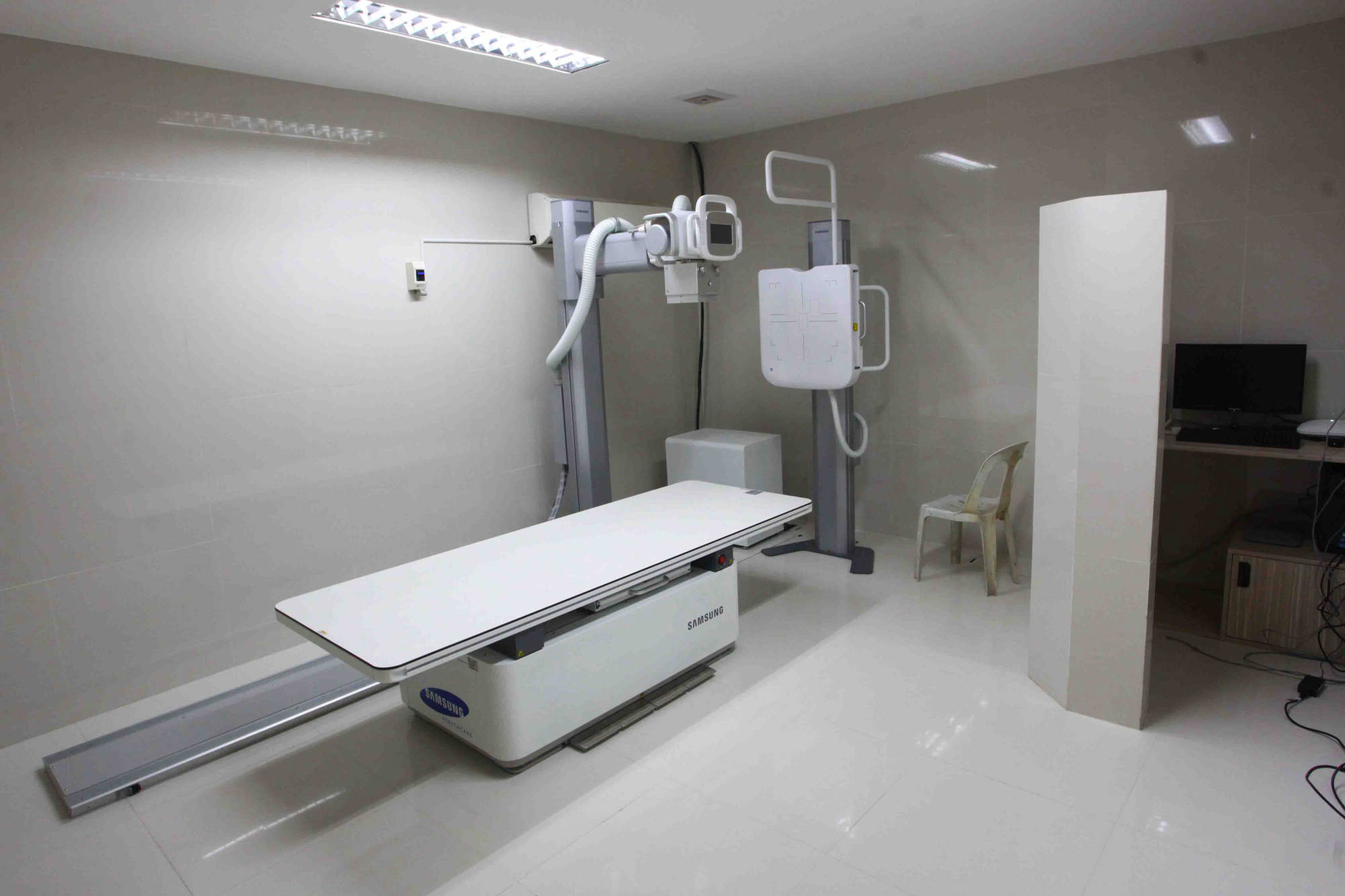
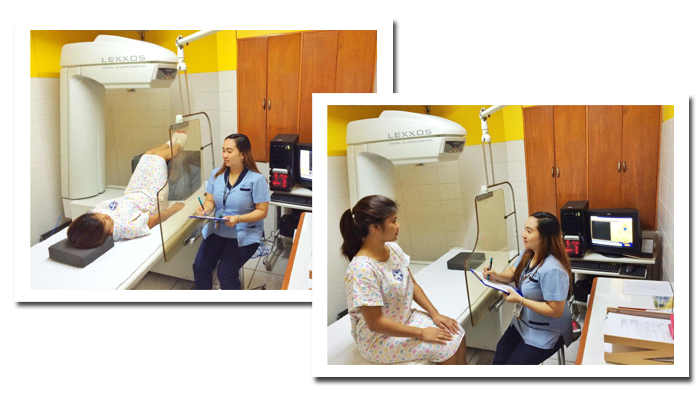
A bone density test is a measurement of the density of your bone mineral, and can be taken from various places throughout the body. A bone density test involves the use of x-ray, in low dosage, and takes only few minutes with virtually no discomfort to the patient. The bone density test is the signle most useful procedure in the diagnosis of osteoporosis and the evaluation of fracture risk. The lower your bone density, the higher your risk of fracture.
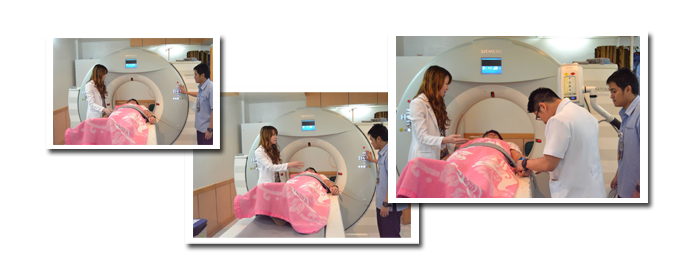
It uses X-rays to create numerous cross-sectional images of the body. CT is used to diagnose disease and injury in many parts of the body such as trauma, oncology, gastrointestinal care, postoperative evaluation, chest disorders, orthopedics, and angiographies. CDUH's advance CT imaging systems (Siemens Definition AS+ 128-Slice),with precise and rapid imaging of the body, provide highly detailed three-dimensional images which can be used to diagnose common and hard-to-detect conditions in areas such as the head (stroke assessment), neck, chest, heart and blood vessels, abdomen, lungs, colon, and legs.
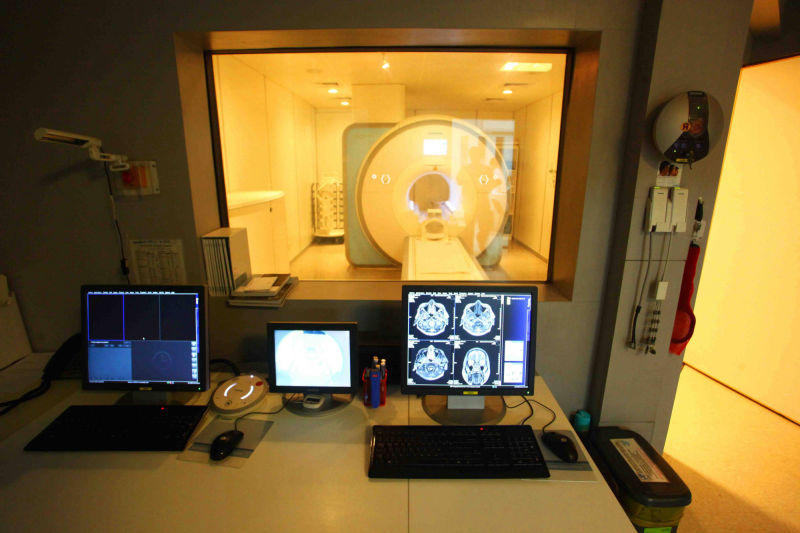
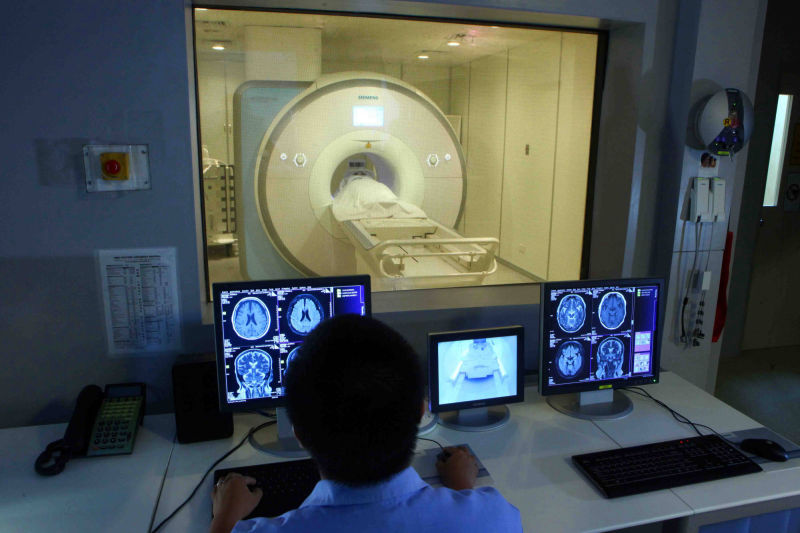
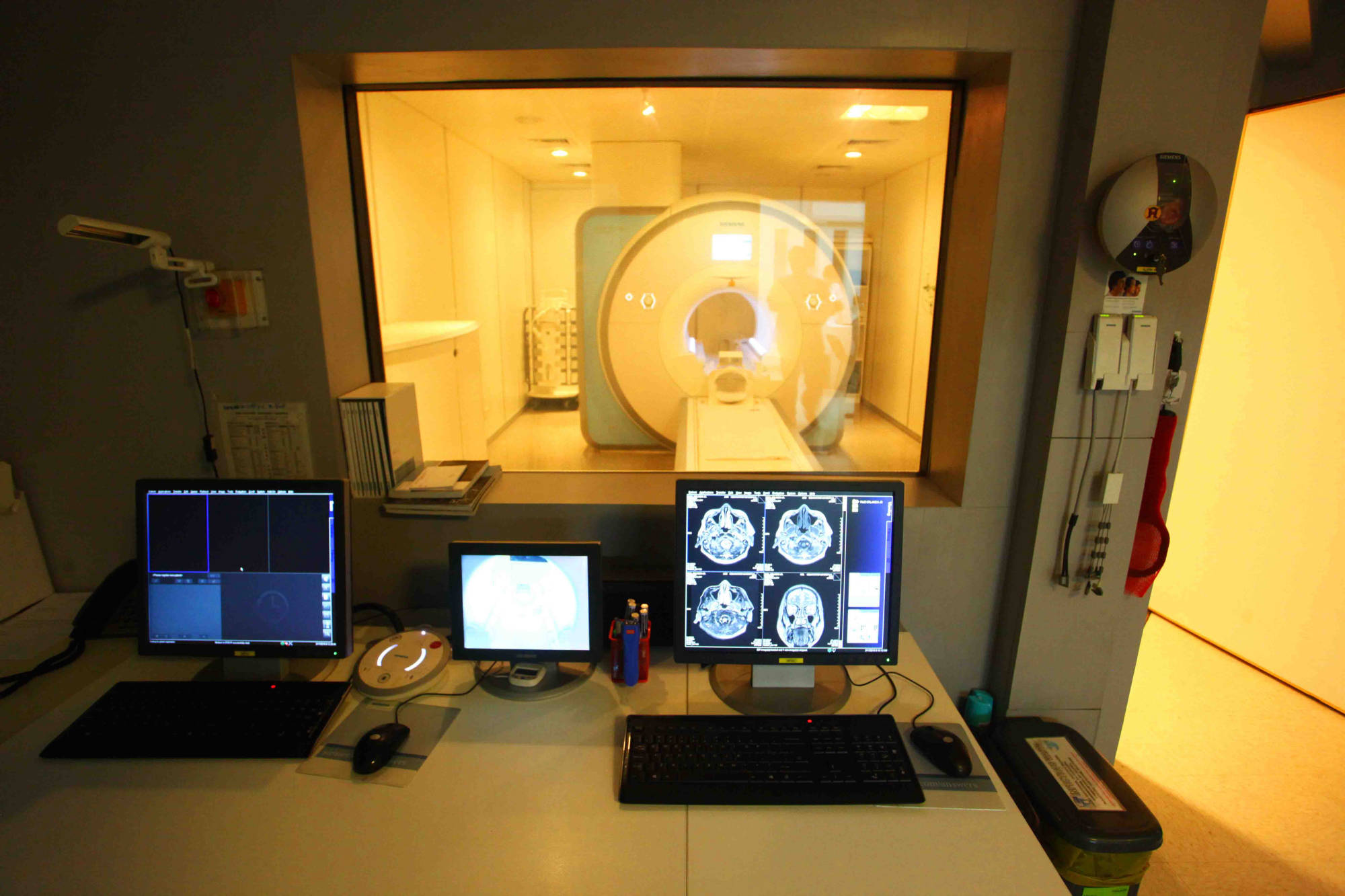
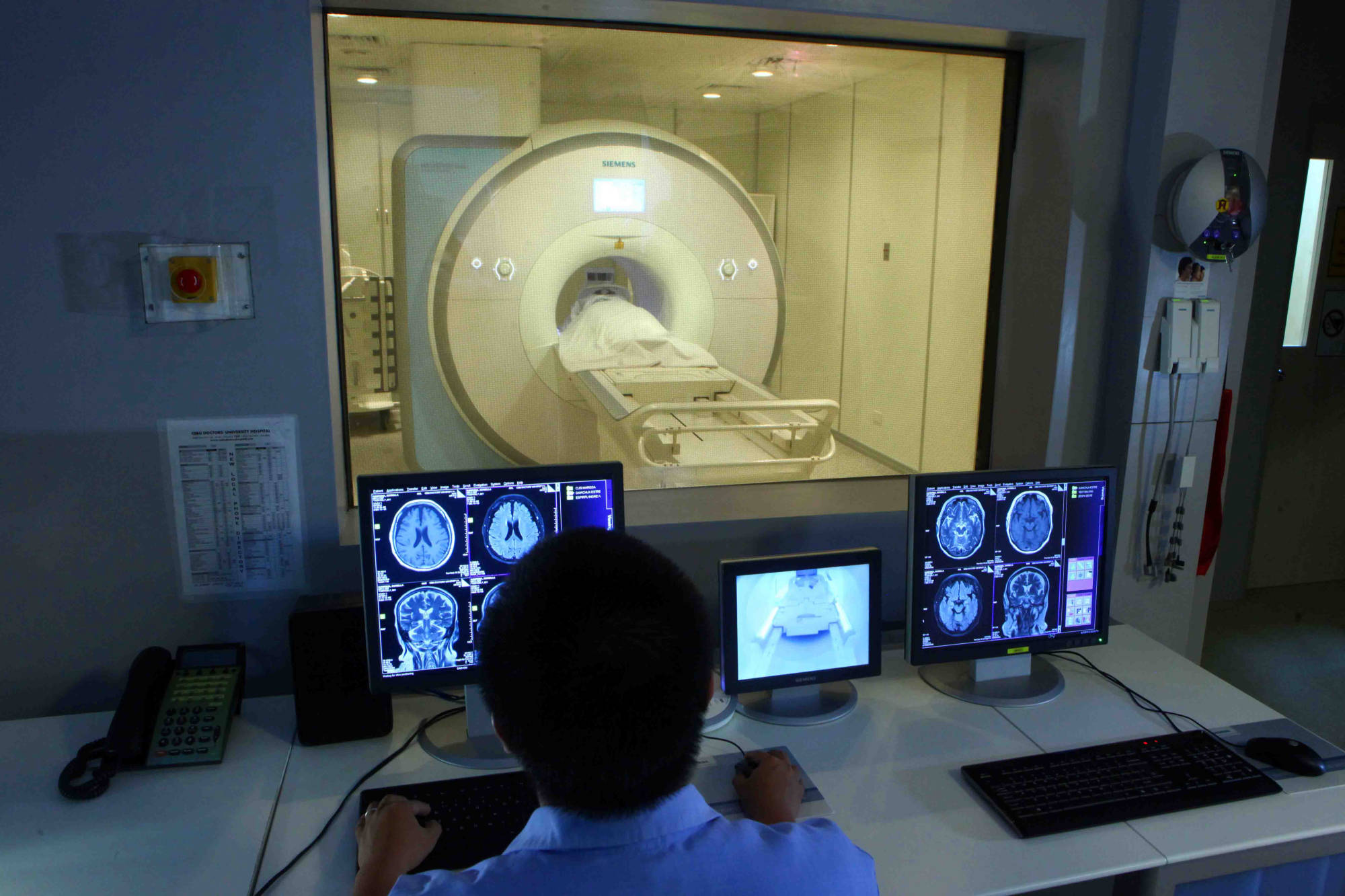
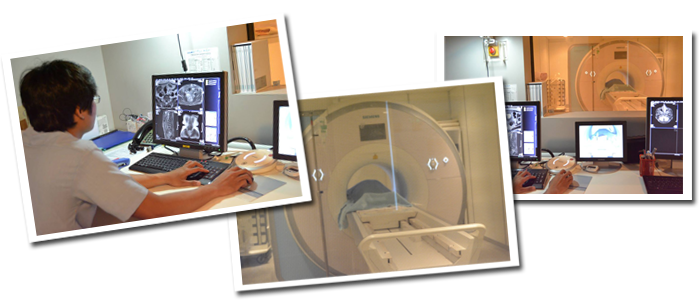
An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is a radiology technique that uses magnetism, radio waves, and a computer to produce images of body structures. The MRI scanner is a tube surrounded by a giant circular magnet. The patient is placed on a moveable bed that is inserted into the magnet. The magnet creates a strong magnetic field that aligns the protons of hydrogen atoms, which are then exposed to a beam of radio waves. This spins the various protons of the body, and they produce a faint signal that is detected by the receiver portion of the MRI scanner. The receiver information is processed by a computer, and an image is produced.
MRI SCAN FACTS:
- MRI scanning uses magnetism, radio waves, and a computer to produce images of body structures.
- MRI scanning is painless and does not involve x-ray radiation
- Patients with heart pacemakers, metal implants, or metal chips or clips in or around the eyes cannot be scanned with MRI because of the effect of the magnet.
- Claustrophobic sensation can occur with MRI scanning.
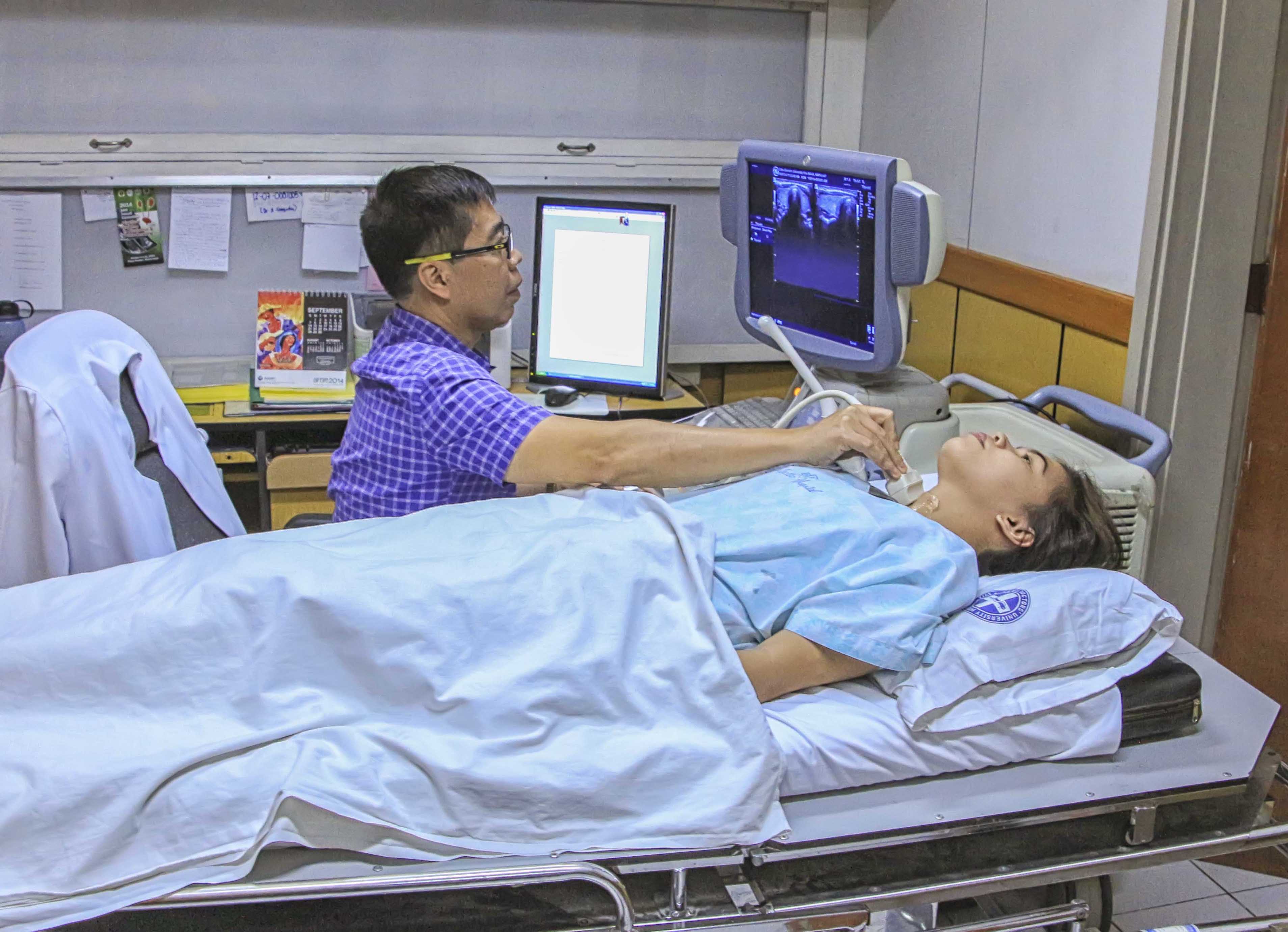
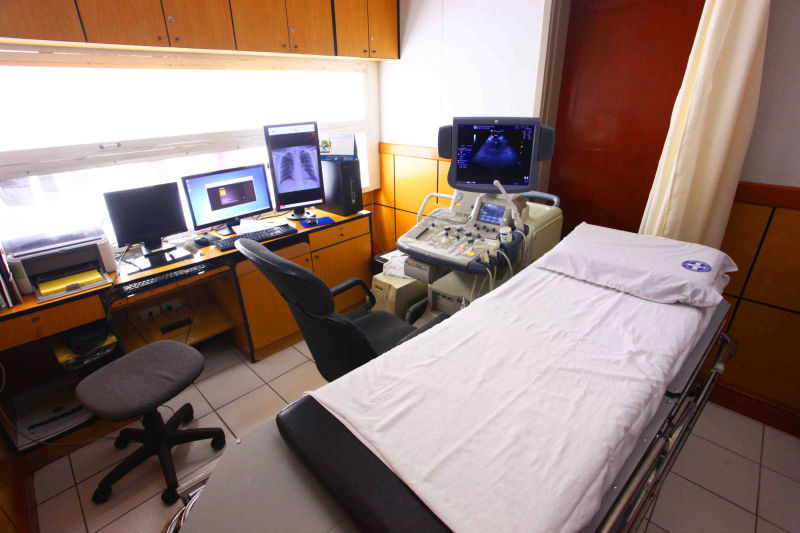
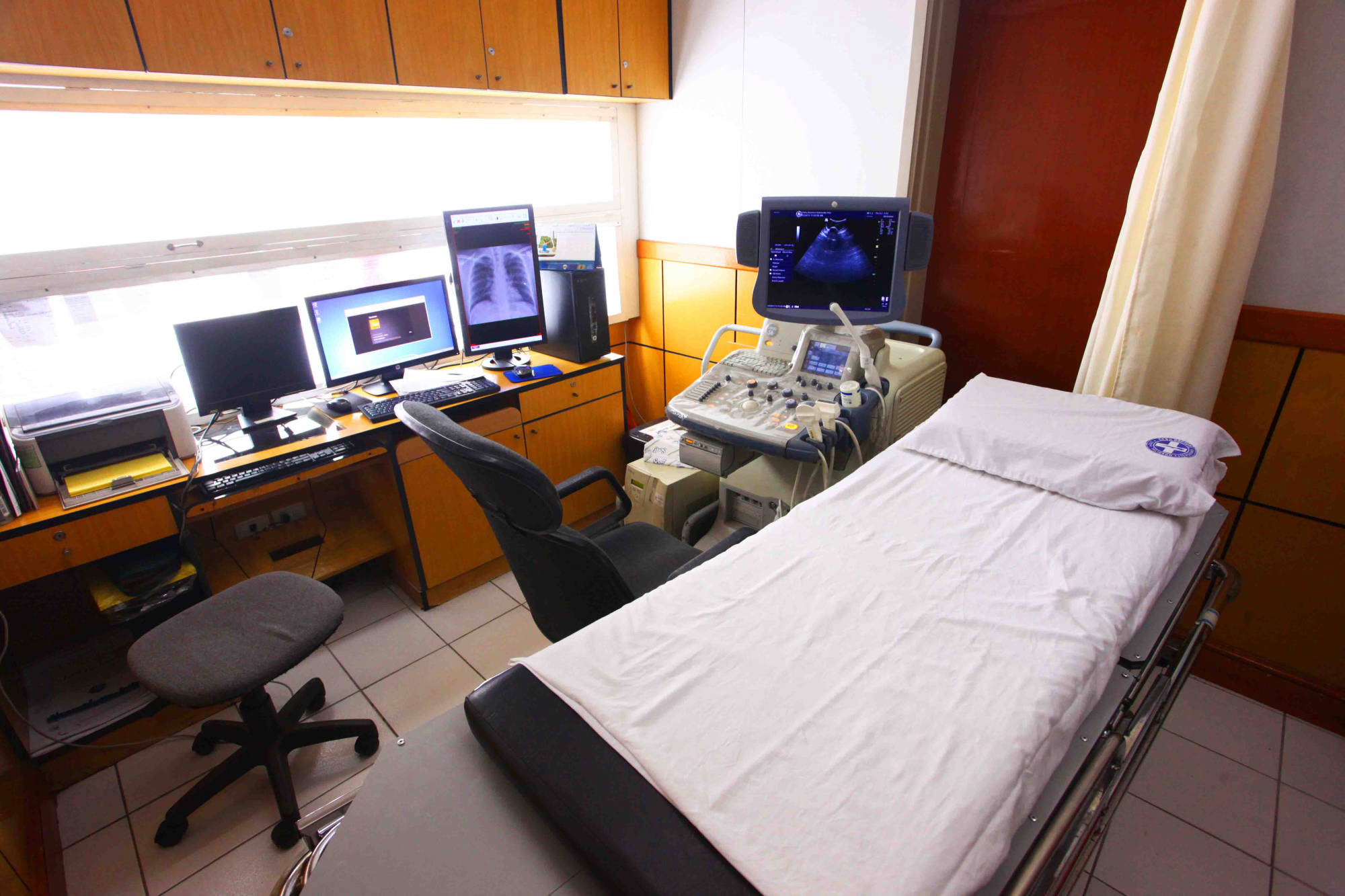
It is safe and painless, and produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging, also called ultrasound scanning or sonography, involves the use of a small transducer (probe) and ultrasound gel placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves are transmitted from the probe through the gel into the body. The transducer collects the sounds that bounce back and a computer then uses those sound waves to create an image. Ultrasound examinations do not use ionizing radiation (as used in x-rays), thus there is no radiation exposure to the patient. Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can show the structure and movement of the body's internal organs, as well as blood flowing through blood vessels.